Handshake - What is it and why is it important?
When it comes to the evolution of the internet and how we use it, you can wait for crucial changes to come and struggle to react and adapt to them, or you can anticipate the changes ahead of time and prepare for them. Part of being prepared is staying on top of current trends and understanding how they will impact the future of your business.
That’s why you should familiarize yourself with Handshake, an innovative TLD registry that answers the accessibility issues of the traditional Domain Name System.
Before describing the potential benefits of getting involved with Handshake, let’s break down what it means:
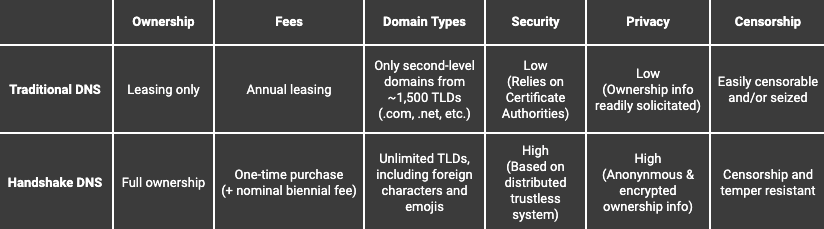
Currently, the rights to TLDs (Top Level Domains) are leased to users by a centralized authority known as ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
What exactly is a TLD?
TLDs are the suffix segments that are found in domains after the “.” symbol and make up the highest rank of the hierarchical Domain Name System of the Internet after the root domain. Common TLDs include “.com”, “.org”, and “.net”.
Where does ICANN Come in?
ICANN is an international, non-profit corporation that manages internet protocol, address space allocation, TLDs, and more. Up until now, ICANN’s involvement in TLDs has created a large barrier to entry for individuals and businesses seeking to own new domains.
Handshake’s Solution
Handshake seeks to provide users with a naming solution that is superior to what ICANN can provide in terms of accessibility, affordability, and nuance.
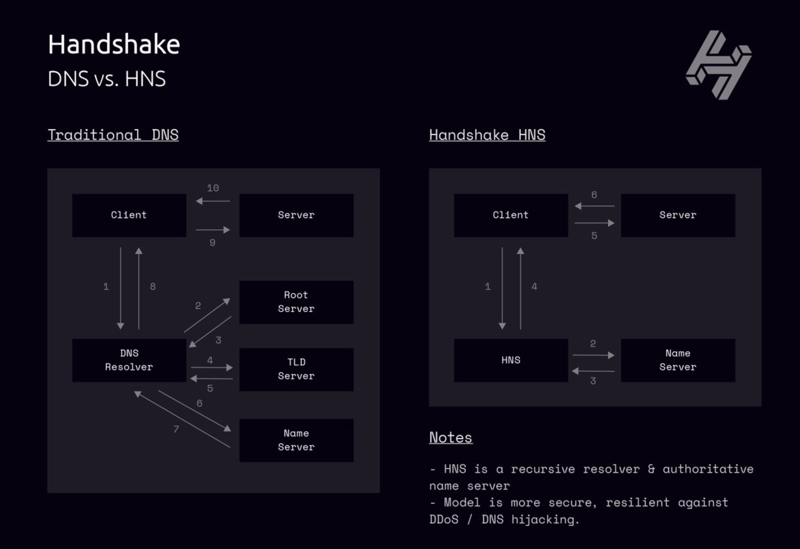
Handshake is a new protocol for administering ownership (ownership, not leased) rights to Top Level Domains on the internet. It is blockchain-powered, decentralized, and permissionless, with users themselves in charge of maintaining their new root Domain Name System.
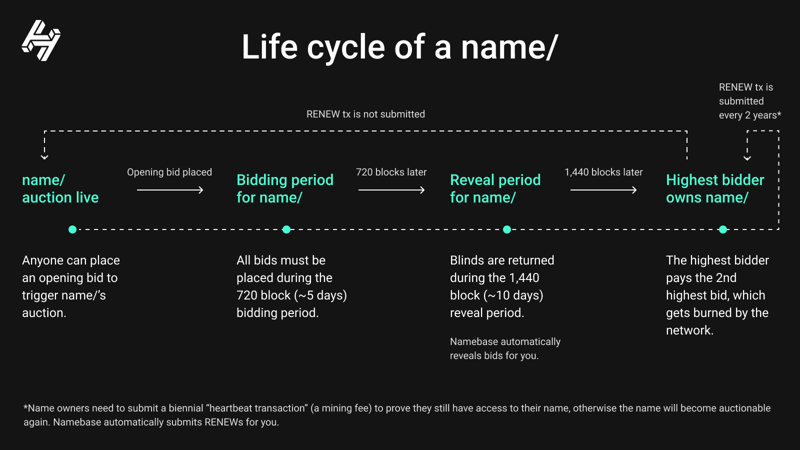
Instead of replacing the current DNS protocol, Handshake replaces the root zone file–that stores TLD ownership–and the root servers with its blockchain system that is accessible to all. Names get registered into the Handshake blockchain by anyone who wishes, and it serves as a large, distributed zone file. Users can register domains to this blockchain by visiting Namebase, a domain registrar and marketplace for Handshake names, and using the handshake coin (HNS) to bid on names.
**It is important to note that Handshake is not meant to compete with the traditional Domain Name System that’s in place. Instead, it is compatible with it, and made to give web surfers access to all of the same domains while still offering access to its own alternative domains.
What is the point of a new naming solution for the internet?
First off, a new naming solution seeks to improve accessibility for anyone in need of a domain. Handshake answers this by making names on the platform exempt from following the conventions upheld by ICANN. For example, if your name was John Doe and you ran an auto repair business you might want to register the name “https://autorepair.johndoe” on the traditional Domain Name System. Unfortunately, ICANN wouldn’t create the Top Level Domain “.johndoe” for you. However, on Handshake, it would be allowed.
This ability is certainly appealing to small and medium-sized businesses who seek greater independence when it comes to establishing an effective domain. But this perk is not Handshake’s main draw…
At its core, Handshake takes an innovative approach to the accessibility of the web. The platform is a step toward a web that is open, free, secure, and private. With the topic of internet censorship becoming a prime topic of interest in our social and political realms, it’s now clear that the current Domain Name System as managed by ICANN is vulnerable to censorship, surveillance, and hacking. Handshake offers itself as an alternative system that resists censorship, surveillance, and hacking because of its decentralized nature.

What does this mean for me?
Handshake is a project that has many passionate developers surrounding it, and it may mark the beginning of a transition to web3 and a new era of internet use.
The internet as we know it, also referred to as web 2.0, is one that involves users creating value for the owners of the site. Social media has become the norm, and users generate most of the content out there however they do not control their own content. Their host websites often own their data and can get rid of their content at any time if it doesn’t abide by their terms or threatens profit.
Web3 is developing as a reaction to the aforementioned perils that have arisen from web 2.0. It is an attempt to bring power back to the people, allowing users to reap the benefits of the value that they create. Web3 applications are built on decentralized, peer-run networks that are operated and maintained by users themselves instead of companies. These networks are self-organizing and resistant to censorship.
You can think of web3 as a future internet in which individuals are enabled to contribute their time and data and be compensated for it rather than be exploited by large, centralized third parties. The platform Namebase is one part of this shift toward a freer web. It has already helped users register hundreds of thousands of names with their marketplace processing over 10k+ sales.
Stay Tuned
Foresight and anticipation of market trends are important aspects of success. This article is the first installment in a series that will be explaining the ins and outs of Handshake and Namebase to help keep you informed. In our next article, we will further explore the bidding process for registering domains in the Nambase marketplace. Want more updates and insights on new technology and advancements? Subscribe to our Tech Tidbits newsletter below.






